Transient blood-brain barrier opening via brain subsystem stimulation
Overview
One of the primary obstacles of delivering pharmacological agents to the brain is the blood-brain barrier (BBB). This technology describes methods for selectively opening the BBB by stimulating dopaminergic neurons in specific areas of the midbrain, particularly the ventral tegmental area (VTA) and substantia nigra pars compacta. The key innovation is that BBB permeability can be increased through non-invasive behavioral stimuli like rewards or reward anticipation and through direct stimulation methods like optogenetics or deep brain stimulation. This controlled BBB opening can allow for enhanced delivery of therapeutic drugs to the brain and improved clearance of disease-related debris, potentially benefiting treatment of neurological conditions. The technology demonstrates that BBB permeability can be modulated with sub-millimeter and sub-second precision, and that timing rewards with drug administration could improve therapeutic delivery to the brain.
Market Opportunity
The market opportunity is substantial, addressing a critical challenge in central nervous system (CNS) drug development and delivery. With approximately 98% of small molecules and nearly all large therapeutic molecules unable to cross the BBB naturally, this innovation could unlock new potential for treating numerous neurological conditions. The technology could particularly impact treatment of major CNS disorders like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, brain cancers, and stroke. The CNS therapeutics market was valued at $114.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% from 20224 to 2033 and reach $199.1 billion. Additionally, enabling better CNS drug delivery could help rescue the many CNS therapeutic candidates that currently fail in clinical trials due to poor brain penetration.
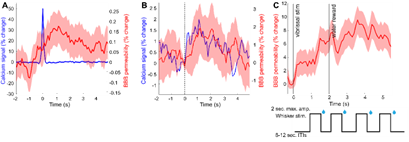
- Individual DA (VTA axon calcium) spikes predict increased BBB permeability.
- Optogenetic drive of VTA-DA neurons increases BBB permeability.
- Behaviorally driven VTA-DA neuron activity increases BBB permeability.
Innovation and Meaningful Advantages
This invention represents a significant advance in drug delivery to the brain by leveraging the brain's natural reward pathways to open the BBB temporarily. Unlike traditional methods that often require invasive procedures or cause widespread BBB disruption, this approach can enable precise spatial and temporal control through behavioral stimuli or targeted neural activation. The ability to coordinate BBB opening with drug administration, particularly through simple reward-based tasks, makes this method uniquely practical for clinical applications with several key advantages:
- First demonstration that BBB permeability can be controlled through behavioral rewards and natural dopaminergic signaling, rather than just through direct physical/chemical interventions
- Introduces temporally precise control (sub-second) of BBB opening that can be coordinated with drug administration
- Non-invasive control through behavioral stimuli (like rewards), eliminating the need for surgical intervention
- Dual therapeutic benefit - enables both enhanced drug delivery into the brain and improved clearance of disease-related waste products, particularly relevant for neurodegenerative conditions
Collaboration Opportunity: We are interested in exploring research collaboration opportunities.
References
|
Principal Investigator
Christopher Moore, PhD
Clinical Professor of Neuroscience
Brown University
christopher_moore@brown.edu
https://vivo.brown.edu/display/cm78
|
Contact
Melissa Simon
Director of Business Development
Brown Technology Innovations
melissa_j_simon@brown.edu
Brown Tech ID 3277
|