Burr Hole Mounted Frameless Stereotactic Device
Overview
The ability to visualize a surgical field and navigate to the appropriate region of interest is imperative during minimally invasive surgeries. Stereotactic image guidance is an intervention which utilizes 3D imaging technology to locate targets of interest, such as tumors and/or lesions, during surgeries where visualization can be restricted, such as in neurosurgeries. In practice, intraoperative CT/MRI scanning is performed with fiducial markers which allow surgeons to render a 3D image of the surgical field that can be correlated with these markers to generate an accurate coordinate system. The disclosed technology outlines a novel stereotactic device for neurosurgery which does not require a traditional metal frame, leading to reduced scanning and fitting time, increased scan relevance and shorter procedure times in stereotactic neurosurgeries.
Market Opportunity
It is estimated that 13.8 million neurosurgical procedures occur globally each year. Currently, stereotactic image-guided surgeries utilize a metal frame, called a stereotactic head frame, which is secured to a patient’s skull by four pins in a procedure requiring local anesthesia. These pins are utilized as reference points during imaging and surgery. Yet, complications with this procedure can occur including patient pain, shifting of the frame, and increased procedural times. The disclosed device presents an alternative in the form of a frameless stereotactic device which is secured through a standard burr hole and features rigidly mounted fiducial markers for image-guided stereotactic surgeries. This device advances a personalized medicine approach to patient care, as the unique structure of a patient’s brain and/or specific disease can be accommodated. Such an approach has applications in neurosurgeries including biopsies, cranial radiotherapy, implantation of deep brain stimulators and placement of depth electrodes.
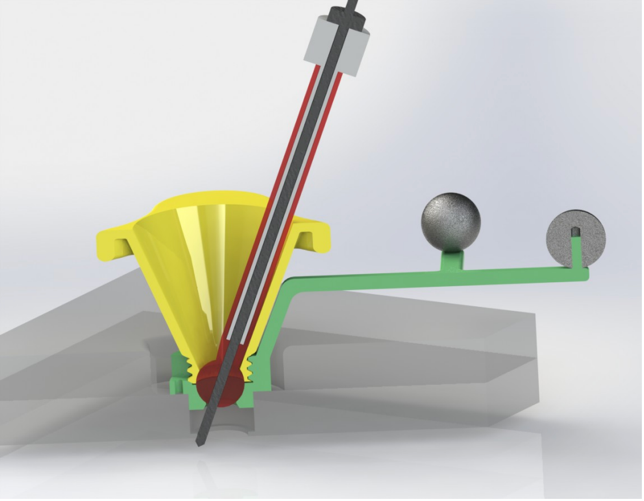
Innovation and Meaningful Advantages
The disclosed device technology addresses the limitations of the current stereotactic head frames in attachment, flexibility and ease of use. This device has a secure, adaptable mount for attachment to a patient’s skull through a standard 14mm burr hole. The fiducial markers are thus rigidly mounted to a patient’s skull, limiting accidental shifts and the need for additional surgical arms and frames. Further, the ball joint of the device allows enhanced flexibility of the guide to precisely locate difficult to reach locations and has the ability to lock desired angles into place for security during imaging. These unique design features enable better targeting within the brain, streamlines stereotactic surgical imaging and results in increased scan relevance and shorter procedural times. This device can be readily adapted to a variety of neurosurgeries that require image guidance.
Collaboration Opportunity
We are interested in exploring research collaborations and licensing opportunities
References
|
Principal Investigator
Rees Cosgrove, MD, FRCSC
Professor Emeritus of Neurosurgery
Warren Alpert School of Medicine at Brown University
|
Contact
Melissa Simon, PhD
Director of Business Development
Brown Technology Innovations
melissa_j_simon@brown.edu
Brown Tech ID 2255
|